 Childhood obesity remains a significant public health concern and is most widespread in low-income households, where barriers to wellness are highest. Addressing this problem requires family-focused approaches as the household environment influences behaviors in many ways. For example, when parents model healthy behaviors such as nutritious eating and physical activity, children are more likely to engage in these behaviors. Yet, socioeconomic stressors can make it challenging to find the time, energy, and motivation to eat healthfully and be physically active.
Childhood obesity remains a significant public health concern and is most widespread in low-income households, where barriers to wellness are highest. Addressing this problem requires family-focused approaches as the household environment influences behaviors in many ways. For example, when parents model healthy behaviors such as nutritious eating and physical activity, children are more likely to engage in these behaviors. Yet, socioeconomic stressors can make it challenging to find the time, energy, and motivation to eat healthfully and be physically active.
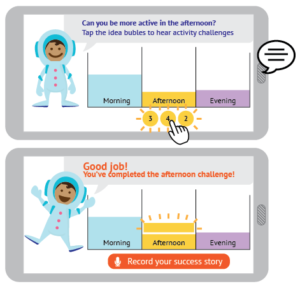
The proposed work examines how experiential learning technologies can help families overcome such barriers by learning and applying meaningful insights from sensor-collected data about their physical activity. Human-Computer Interaction researchers have shown the value of information and communication technologies that enable the visualization of such data. However, there has been limited work examining how technology can help low-income families learn from this data and overcome wellness barriers. Motivated by research demonstrating the power of games as learning environments, the proposed work will establish the design space of experiential learning technologies that help families develop healthier behaviors.
In the first phase of this research, we are conducting formative research to assess factors such as the impact of socioeconomic context and household structure on the management of and attitudes towards wellness data in families.
Our primary goals are to produce:
- Fundamental knowledge about the structural and socioeconomic characteristics of the family, and its implications in design of Experiential Learning Technologies and health tracking tools in general,
- Insights on how game-based displays of behavior modeling can encourage benefits previously documented for traditional in-person modeling and,
- 3. A novel experiential learning game that supports under-researched learning processes and evidence showing its efficacy in low-income families.
The work will also have a significant broader impact by:
- Demonstrating how experiential learning technologies can be a sustainable and engaging way of encouraging physical activity,
- Nurturing interest in children who have traditionally been underrepresented in the field of computer science by engaging them through participatory workshops,
- Improving the participant’s understanding of their bodies in a socially and socio-economically relevant way and,
- A service-learning curriculum which will let students practice course concepts during the participatory design portion of the proposed work.
The research is being conducted in partnership with the Boston Centers for Youth and Families and the Mattapan Food & Fitness Coalition. This project received a 3-year grant from the National Science Foundation.
People
- Our project team is comprised of an interdisciplinary group of faculty, students, and community partners:
- Andrea G. Parker, PhD, Principal Investigator
- Carmen Sceppa, MD, PhD, Co-Principal Investigator
- Jessica Hoffman, PhD, Co-Principal Investigator
- Magy Seif El-Nasr, PhD, Co-Principal Investigator
- Herman Saksono, Computer Science PhD Student
Partner Organizations
Materials
Publications
- Herman Saksono, Carmen Castaneda-Sceppa, Jessica Hoffman, Magy Seif El-Nasr, Vivien Morris, and Andrea G. Parker. 2019. Social Reflections on Fitness Tracking Data: A Study with Families in Low-SES Neighborhoods. To appear in Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI 2019). (PDF)
- Herman Saksono, Carmen Castaneda-Sceppa, Jessica Hoffman, Magy Seif El-Nasr, Vivien Morris, Andrea Parker. 2018. Family Health Promotion in Low-SES Neighborhoods: A Two-Month Study of Wearable Activity Tracking. In Proceedings of the 2018 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI 2018). ACM, New York, NY, USA. (PDF)
- Parker, A.G., Saksono, H., Hoffman, J. and Castaneda-Sceppa, C., “A Community Health Orientation for Wellness Technology Design & Delivery,” in Ackerman, M., Prilla, M., Stary, C., Hermann, T. and Goggins, S. (eds.), Designing Healthcare That Works: A Sociotechnical Approach, Elsevier (Nov 2017).
- Herman Saksono and Andrea G. Parker. 2017. Reflective Informatics Through Family Storytelling: Self-discovering Physical Activity Predictors. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. (PDF).
News
- Fitness Trackers Need to go Beyond Counting Steps. Here’s Why. Laura Castañón. News @ Northeastern. May 22, 2019.
- When is a Fitbit like a New Year’s resolution? Bill Ibelle. Bouvé. May 10, 2019.
This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant Number #1618406. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
